Multimodal RAG
Author: Kane
Design: Kane
Proofread : JaeJun Shim
This is a part of LangChain Open Tutorial
Overview
This tutorial demonstrates how to build a Multimodal RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system using LangChain. The system processes both text and images from documents, creating a unified knowledge base for question-answering.
Key features include:
Text content extraction to markdown using
pymupdf4llmImage content extraction using
Upstage Document AI APIText and image content merging by page
RAG implementation using
OpenAI embeddingsandGPT-4oLanggraphbased RAG pipeline

Table of Contents
References
Environment Setup
Set up the environment. You may refer to Environment Setup for more details.
[Note]
langchain-opentutorialis a package that provides a set of easy-to-use environment setup, useful functions and utilities for tutorials.You can checkout the
langchain-opentutorialfor more details.
Extract and preprocess Text contents from PDF using PyMuPDF4LLM
PyMuPDF4LLMPyMuPDF4LLM
PyMuPDF4LLMPyMuPDF4LLM is a Python package designed to facilitate the extraction of PDF content into formats suitable for Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) environments. It supports Markdown extraction and LlamaIndex document output, making it a valuable tool for developing document-based AI applications.
Key Features
Multi-Column Page Support: Accurately extracts text from pages with multiple columns.
Image and Vector Graphics Extraction: Extracts images and vector graphics from pages, including references in the Markdown text.
Page Chunking Output: Outputs pages in chunks, facilitating use in LLM and RAG systems.
LlamaIndex Document Output: Directly converts PDFs into LlamaIndex document format.
Layout parsing to extract image from PDF using Upstage Document Parse API
Upstage Document Parse APIThe Upstage Document Parse API is a robust AI model that converts various document formats, including PDFs and images, into HTML by detecting layout elements such as paragraphs, tables, and images. This facilitates the integration of document content into applications requiring structured data.
Key Features:
Layout Detection: Identifies and preserves document structures, including paragraphs, tables, and images.
Format Conversion: Transforms documents into HTML, maintaining the original layout and reading order.
High Performance: Processes documents swiftly, handling up to 100 pages per minute.
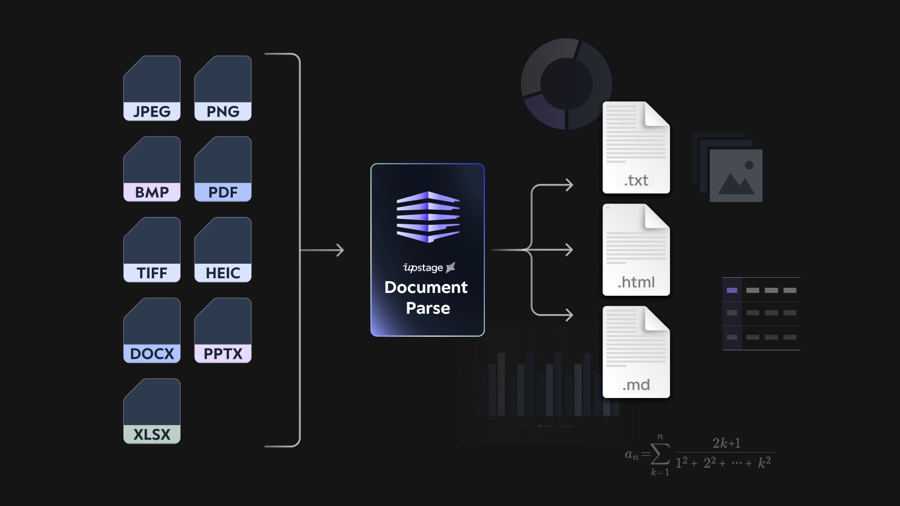
Source: Upstage Official Website
UpstageDocumentParseLoader in LangChain
UpstageDocumentParseLoader in LangChainThe UpstageDocumentParseLoader is a component of the langchain_upstage package that integrates Upstage's Document Parser API into the LangChain framework. It enables seamless loading and parsing of documents within LangChain applications.
Inspect parsed documents to check for and display base64-encoded content along with a brief summary of each document's content and metadata.

This process generates multimodal descriptions of images detected on each page using the Gemini 1.5 Flash 8B API. These descriptions are combined with the previously extracted text to create a complete embedding, enabling a RAG pipeline capable of understanding images as well.
Building a RAG Pipeline with LangGraph
LangGraphThis guide demonstrates how to use LangGraph to build a unified RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) application. By combining retrieval and generation into a single flow, LangGraph offers streamlined execution, deployment, and additional features like persistence and human-in-the-loop approval.
Key Components
Application State:
Tracks input (
question), intermediate (context), and output (answer) data using aTypedDict.
Application Steps:
Retrieve: Uses
Chromafor similarity-based document retrieval.Generate: Formats retrieved context and question, then invokes
ChatOpenAIto generate an answer.
Control Flow:
Uses
StateGraphto define the sequence and connections between steps.
As shown in the image below, the answer was correctly predicted.

Last updated