Using the OpenAI API (GPT-4o Multimodal)
Author: Erika Park
Peer Review: JeongGi Park, Wooseok Jeong
Proofread : Q0211
This is a part of LangChain Open Tutorial
Overview
This tutorial explains how to effectively use OpenAI's GPT-4o multimodal model with LangChain, a versatile framework for building language model applications. You'll learn to set up and work with the ChatOpenAI object for tasks such as generating responses, analyzing model outputs, and leveraging advanced features like real-time response streaming and token log probability analysis. By the end of this guide, you'll have the tools to experiment with and deploy sophisticated AI solutions smoothly and efficiently.
Table of Contents
References
Environment Setup
Set up the environment. You may refer to Environment Setup for more details.
[Note]
langchain-opentutorialis a package that provides a set of easy-to-use environment setup, useful functions, and utilities for tutorials.You can checkout out the
langchain-opentutorialfor more details.
You can alternatively set API keys such as OPENAI_API_KEY in a .env file and load them.
[Note] This is not necessary if you've already set the required API keys in previous steps.
ChatOpenAI GPT-4o Multimodal
This is a chat-specific Large Language Model (LLM) provided by OpenAI.
When creating an object, the following options can be specified. Details about the options are as follows:
temperature
Specifies the sampling temperature, which can be chosen between 0 and 2. A higher value, such as 0.8, results in more random outputs, while a lower value, such as 0.2, makes the outputs more focused and deterministic.
max_tokens
The maximum number of tokens to generate for the chat completion.
model_name : List of available models
gpt-4ogpt-4o-minio1-preview,o1-preview-mini: Available only for Tier 5 accounts, which require a minimum recharge of $1,000 to access.

Link: https://platform.openai.com/docs/models
Response Format (AI Message)
When using the ChatOpenAI object, the response is returned in the format of an AI Message. This includes the text content generated by the model along with any metadata or additional properties associated with the response. These provide structured information about the AI's reply and how it was generated.
Key Components of AI Message
contentDefinition: The primary response text generated by the AI.
Example: "The capital of South Korea is Seoul."
Purpose: This is the main part of the response that users interact with.
response_metadataDefinition: Metadata about the response generation process.
Key Fields:
model_name: Name of the model used (e.g.,"gpt-4o-mini").finish_reason: Reason the generation stopped (stop for normal completion).token_usage: Token usage details:prompt_tokens: Tokens used for the input query.completion_tokens: Tokens used for the response.total_tokens: Combined token count.
idDefinition: A unique identifier for the API call.
Purpose: Useful for tracking or debugging specific interactions.
Activating LogProb
LogProbLogProb represents the logarithmic probabilities assigned by the model to predicted tokens. A token is an individual unit of text, such as a word, character, or part of a word. The probability indicates the model's confidence in predicting each token.
Use Cases:LogProb is useful for evaluating the model's prediction confidence, debugging issues, and optimizing prompts. By analyzing LogProb data, you can understand why the model selected specific tokens.
Caution:
Enabling LogProb increases the response data size, which may affect API speed and cost. It is recommended to activate it only when necessary.
Streaming Output
The streaming option is particularly useful for receiving real-time responses to queries.
Instead of waiting for the entire response to be generated, the model streams the output token by token or in chunks, enabling faster interaction and immediate feedback.
Multimodal AI: Text and Image Processing with GPT-4o
Multimodal refers to technologies or approaches that integrate and process multiple types of information (modalities). This includes a variety of data types such as:
Text: Information in written form, such as documents, books, or web pages.
Image: Visual information, including photos, graphics, or illustrations.
Audio: Auditory information, such as speech, music, or sound effects.
Video: A combination of visual and auditory information, including video clips or real-time streaming.
gpt-4o and gpt-4-turbo are equipped with vision capabilities, enabling them to process and recognize images alongside textual inputs.
Step 1. Setting up ChatOpenAI
First, create a ChatOpenAI object with the gpt-4o model and streaming capabilities enabled.
Step 2. Encoding Images
Images need to be encoded into Base64 format for the model to process them. The following function handles both URL-based and local image files:
Example: Encode and Display an Image
URL-based Image:
Local Image:
Step 3: Creating Messages
Define a function to generate the messages required for the model. This includes:
System Prompt: Defines the role and task for the AI.
User Prompt: Provides the specific task instructions.
Encoded Image: Includes the Base64 image data.
Step 4: Model Interaction
Now, send the generated messages to the model and stream the results in real time.
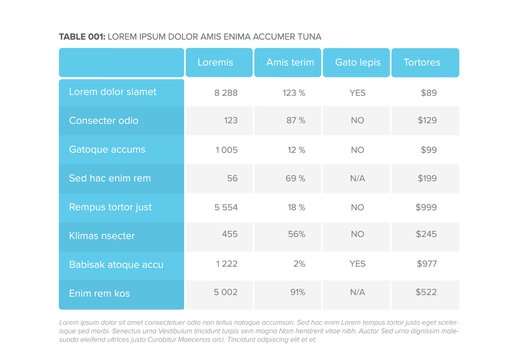
Configuring Multimodal AI with System and User Prompts
This tutorial demonstrates how to configure a multimodal AI using system prompts and user prompts, and how to process and interpret an image-based financial table.
What Are Prompts?
System Prompt Defines the AI's identity, responsibilities, and behavior for the session:
Sets the AI's context, ensuring consistent responses.
Example: "You are a financial assistant specializing in interpreting tables."
User Prompt Gives task-specific instructions to guide the AI:
Specifies what the user expects the AI to do.
Example: "Analyze this financial table and summarize the insights."
Step 1: Set Up the ChatOpenAI Object
The ChatOpenAI object initializes the model with the desired configurations, such as temperature and model type.
Step2: Encode and Display the Image
Images need to be encoded into Base64 format so the AI can process them.
Step 3: Define System and User Prompts
Set up the prompts to guide the AI’s behavior and task execution.
Step 4: Create Messages for the AI
Combine the system prompt, user prompt, and the encoded image into a structured message format.
Step 5: Stream the AI's Response
Use the AI model to process the messages and stream the results in real time.
Last updated